Error Handling
Error handling in Go is an integral part of the language's design philosophy. It follows the principle of "errors are values," emphasizing that error handling should be explicit and straightforward. Go provides a robust mechanism for dealing with errors, ensuring that they are reported and managed effectively throughout the program.
Base on go-errors/errors: errors with stacktraces for go (github.com)
Usage of NewError
NewError(err error, errorType IError, args ...interface{}) IError1. err error
The raw error that may come from function calls or service invocations.
1.1. Error originating from a raw error:
resp, err := helpers.CSVFromInterface(data, []string{"วันที่", "จำนวนผู้ใช้่งานที่ใช้งานล่าสุด"},
[]string{"date", "active_users"})
if err != nil {
return nil, s.ctx.NewError(err, errmsgs.InternalServerError)
}1.2. Error originating from IError:
result, ierr := db.FindAll()
if ierr != nil {
return nil, s.ctx.NewError(ierr, ierr)
}2. errorType IError
An error to be returned for the API response, aiming to conceal the actual error message that may expose sensitive information or provide more accurate error context.
2.1. Create a variable ierror related to the specific issue (emsgs/user.error.go)
var UserNotInDomain = core.Error{
Status: http.StatusBadRequest,
Code: "INVALID_USER_NOT_IN_DOMAIN",
Message: "user not in domain",
}2.2. Utilize the variable:
if user.UserType != consts.DomainAdmin {
return nil, s.ctx.NewError(emsgs.UserTypeInvalid, emsgs.UserTypeInvalid)
}if err != nil {
return nil, m.ctx.NewError(err, errmsgs.DBError)
}if domain.MaxSignUsers < (userindomain + int64(len(input.Users))) {
return c.JSON(emsgs.SignUsersExceedLimit.Status, emsgs.SignUsersExceedLimit)
}3. args ...interface{}
Additional information for debugging purposes when encountering the specified error.
err := utils.Copy(&data, &payload)
if err != nil {
return nil, s.ctx.NewError(err, errmsgs. BadRequest, core.Map{
"data": payload,
"id":
})
}if utils.GetInt64(payload.MaxSignUsers) < signUser {
return nil, s.ctx.NewError(emsgs.MaxSignUsersCannotLessThanSignUsers, ensgs.MaxSignUsersCannot Less ThanSignUsers, payload, id, data)
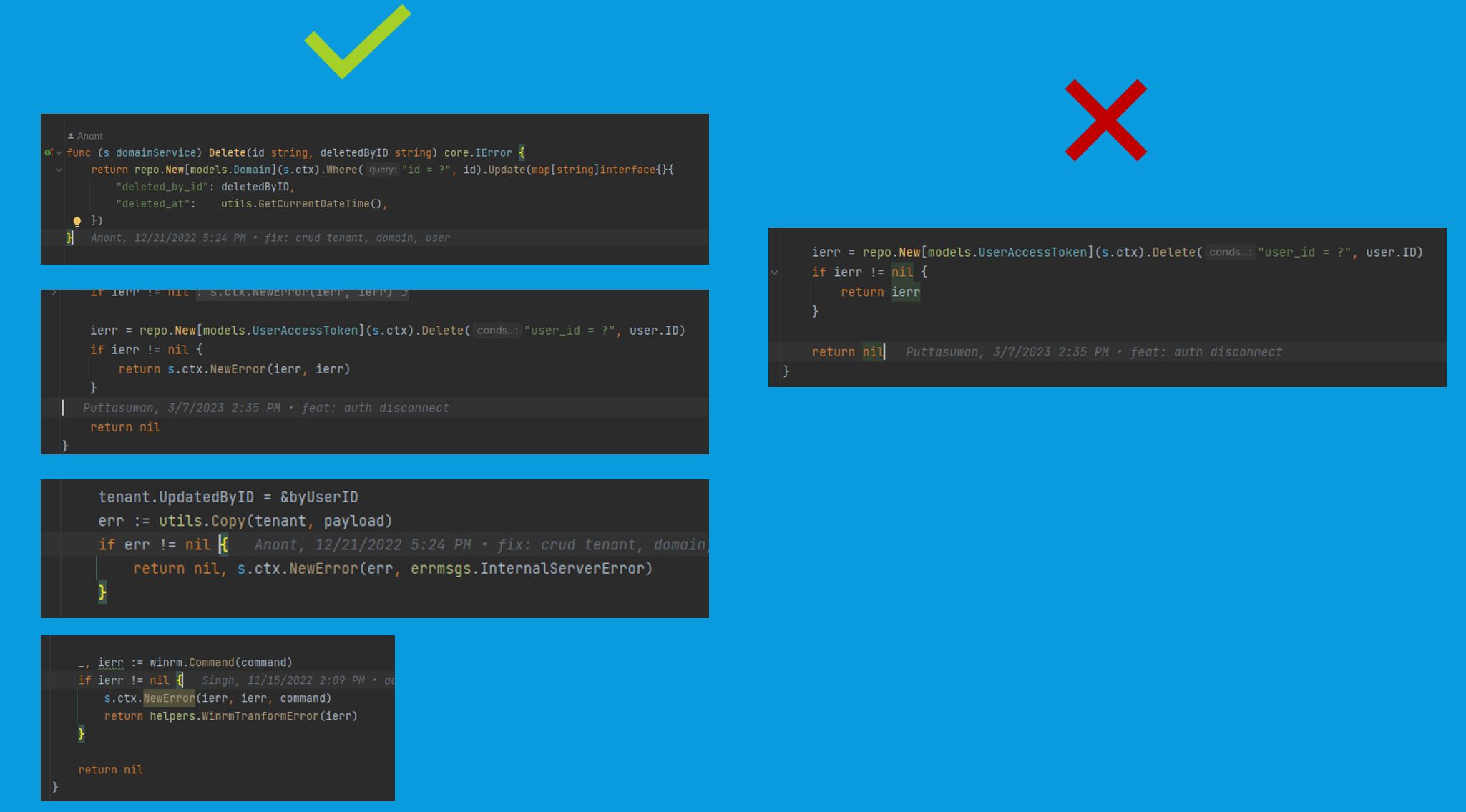
}When should core.IError be returned?
- Every function within the service layer.
- Or functions that are contextually related to the service.
Send to sentry
Update the .env file:
SENTRY_DSN=https://[email protected]/xxxxErrors will be automatically sent to Sentry when NewError is called and the error status is greater than or equal to 500.
Send to graylog
Update the .env file:
LOG_LEVEL=debug|info|warn|error
LOG_HOST=<graylog_ip>
LOG_PORT=<graylog_udp_port>If LOG_LEVEL is set to error, and the error status is greater than or equal to 500 will be sent to Graylog.
If LOG_LEVEL is set to debug, all logs will be sent to Graylog.
Default Error Messages
DBErrorMQErrorCacheErrorCronjobErrorInternalServerErrorNotFoundBadRequestSignatureInValidJSONInValid
Default Error function
IsNotFoundError(err core.IError) boolIsNotFoundErrorCode(code string) boolNotFoundCustomError(key string) core.Error
Conclusion
The document provides examples and visual representations to illustrate the usage of NewError and its different parameters. It demonstrates how errors originating from raw errors or IError can be handled and utilized. It also showcases the use of the error object for API responses and includes additional debugging information.0Fa